What is the heritage?
Heritage is the set of assets acquired by inheritance (…) by title… With regard to culture, set of lifestyles, customs, knowledge and degree of artistic, scientific, industrial development, in an epoch, social group, etc. According to this value we can found: historical heritage, artistic heritage and cultural heritage.
_Cultural asset: the cultural identity is the set of intangigbles features that belong to and define a collective. To identify a culture solely by the set of its monuments (only the great events count) is a mistake. An attitude that ended in the 19th century. In the second half s.XX is formulated the concept of cultural asset (broader) that will integrate objects with historical or artistic value, and also any expression, manifestation or significant testimony of human culture with documentary capacity.
As a result of the Second World War, many countries, interest in objects and activities from hitherto neglected sectors, such as agricultural culture or handicrafts, began to spread. Traditional history has focused on the great political events, military events, scientific conquests, discoveries… that marked the history and therefore the monument constituted its best representation. New history centers its interest in man and his existence, the instruments of work the utensils of everyday use, showing an all-encompassing dimension (which includes everything) and therefore the vestiges to be preserved.
The first use of the term «cultural asset» in an official document was in the 1954 Hague Convention, convened under the patronage of Unesco to agree on the protection of cultural property in the event of armed conflict. It contemplated movable and immovable property with great importance for the culture of the people. In 1972 UNESCO proposed a new classification of cultural property:
-Monuments: architecture, sculpture, painting, archeology, caverns, inscriptions, elements of universal value from the point of view history, art or science.
-Sets: groups of constructions, whose architecture and integration with the landscape give them exceptional value from the historical, art of science point of view.
-Places: works of man and nature with universal value from the historical, aesthetic, ethnological or anthropological point of view.
The law of Patrimonio Hidtórico Español introduces the maximum protection figure: BIC (Asset of Cultural Interest)
Why preserving heritage?
Preservation is a method of not losing the values of cultural identity. In order to preserve before you know what the cultural assets of people are: catalog. All goods contained in catalogues must be protected and preserved. But not only these ones, before any action we make as architects, we must think about the value of the good on which we will intervene before deciding the type of intervention.
What we have to preserve?
Not only the physical architectural heritage but also its values. Every aspect of a building must be taken care of: matter, construction techniques, shapes, dimensions, colours, materials, textures, character, use, environment, meaning.
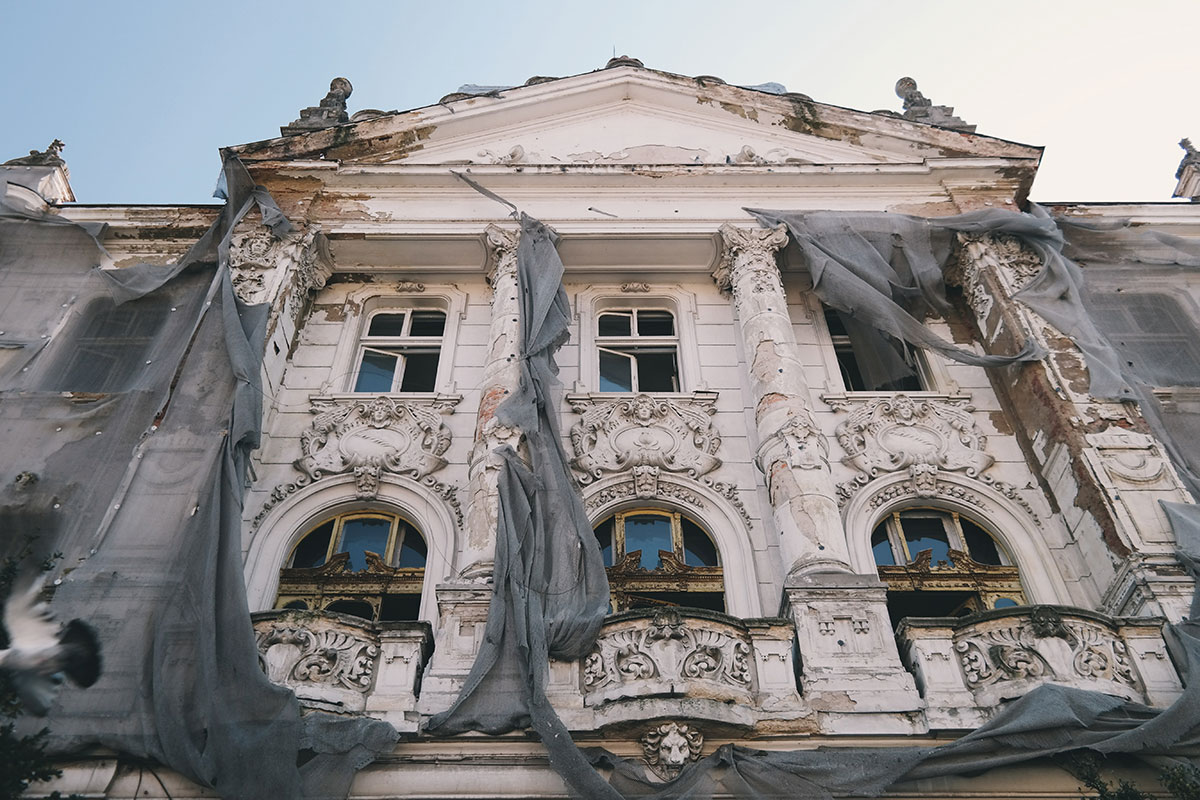

How to preserve?
_Legislative instruments:
-Protect: legal actions, administrative rules outside the intervention of the monument itself. It is exercised through standards or through the development of cataloguing tools. These rules are intended to enshrine the right of the community over the private interest. Different degrees of protection are often differentiated. The conservancy and safeguard are synonymous of protection.
-Inventory: is the result of list, to locate and describe a set of properties. It’s an important instrument for preventive conservation. The LPHE (Spanish Historical Heritage Act) pays great attention to inventories of catalogs.
-To list: The action of cataloguing involves the ennumeration, description and location of a property, but also it provides a historical study and economic valuation of a Heritage Resource. The list is an important instrument of indirect and preventive coservation, as a means of knowledge and valuation of assets.
_Interventions:
-Preservation: operations to be performed on the good to ensure survival against hazards or possible damages. Impact on the preventive aspect. Actions of this type are the decrease of the flow of tourists entering the monument or the reduction of the traffic nearby to avoid emissions of polluting gases.
-Maintenance: continious maintenance, through punctual repairs, in a state of efficiency, in conditions to be used. An operation designed to prolong and mantain as long as possible the materials from which the object is made. Preserve the building’s materials, its character, its meaning, its essence, while maintaining its maximum useful life. The ideal would be continuous and gradual maintenance. Maintenance is one of the most recommended actions to avoid «radical» changes in an historical building.
-Consolidation: is a particular way of preserving; it’s possible thanks to a general strengthening (reinforcement of a structure or of building fabric). The action provides higher consistency and solidity.
-Repairing: fix damaged parts like roofs, walls, eaves, gutters… The concept of reparation is linked to the practice of maintenance.
-Restoration: it supposes a direct intervention on the monument whose purpose is the restitution of improvement of the legibility that is lost with the passage of time, without incurring alterations or falsifications of its documentary nature.
-Adaptation: enable or return something to its old state of efficiency or functionality.
-Reconstruction: it is a procedure of integral or partial reconstruction of the building, with an absolutely exceptional character that has been carried out in specific historical circumstances and as a consequence of traumatic events. It is distinguised from restoration by the introduction of new material.
-Anastilosis (musealización): is an archeological term for a technique whereby a ruined building or monument is rebuilt using original architectural elements. It’s a set of operations to put in place building elements.
-Ripristinar: means returning a building to a known earlier state by removing accretions or by reassembling existing elements. It’s an action that suggest to «go back» to the original state of a building by removing or added later stages. It is an action that tends to be generally rejected because the autenticity and age of the monument is usually lost.